
Product information
Vitamin E is the term for a group of tocopherols and tocotrienols, of which alpha-tocopherol has the highest biological activity. Due to its potent anti-oxidative properties of all tocopherols these are widely used, alpha-tocopherol used in the prevention of chronic diseases. (1)
Its serum concentrations depend on the liver, which takes up the nutrients. The various forms are absorbed from the small intestine. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant which protects cells from the damaging effects of free radicals and these cells contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease and cancer. Vitamin E is involved in immune function, cell signalling, regulation of gene expression and other metabolic processes(2).
The human body also needs vitamin E to boost its immune system so that it can fight off invading bacteria and viruses. It also helps in widening of blood vessels and keep blood from clotting (3) alpha-tocopherol inhibits the activity of protein kinase c, an enzyme involved in cell proliferation and differentiation in smooth muscle cells, platelets and monocytes (4).
Life On Vit E-Life has d alpha tocopheryl acetate which has the highest measurable amount of biological activity when taken through supplement. It maintains highest concentrations in blood when taken as supplement (5).
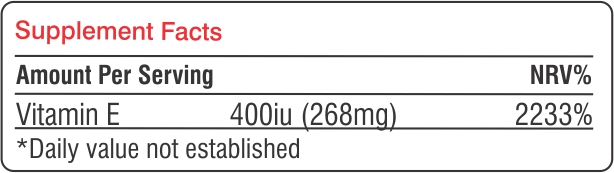
Life On Vit E-Life has 400iu (268mg) of vitamin e providing the complete vitamin e supplement to the consumer.
Vitamin E deficiency is very rare in healthy people. It is almost always linked to certain diseases where fat is not properly digested or absorbed; examples include Crohn's disease, cystic fibrosis and certain rare genetic diseases such as abetalipoproteinemia and ataxia with Vitamin E deficiency (aved).
Vitamin E needs some fat for the digestive system to absorb it. Vitamin E deficiency can cause nerve and muscle damage that results in loss of feeling in the arms and legs, loss of body movement control, muscle weakness and vision problems, another sign of deficiency is a weakened immune system (3).
Vitamin E contributes to the protection of cells from oxidative stress protecting the DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage (6).
References
1)Vitamin E: function and metabolism.faseb j. 1999jul;13(10):1145-55.
2)ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/vitamine-healthprofessional/
3)ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/vitamine-consumer/
4)Dietary reference intakes: vitamin c, vitamin e, selenium and carotenoids institute of medicine. food and nutrition board. Washington, dc: national academy press, 2000.
5)www.livestrong.com/article/485077-is-d-alpha-tocopheryl-acetate-a-natural-form-of-vitamin-e
6)European Union Register on Nutritional and Health Claims.
