
Product information
Multivitamins are natural substances that your body needs to grow, develop and function normally, when your body needs more Vitamins than usual. Multivitamins should be taken who need extra Vitamins, who cannot eat enough food to obtain the required Vitamins or who cannot receive the Vitamins from food they eat (1).
Vitamins are key micronutrients that do not provide energy but play an important role in physiological function and energy metabolism. Minerals, such as Calcium, Iron, Potassium, Sodium and Magnesium are also micronutrients which assist in the creation of body tissues i.e. bones, maintenance of fluid balance and muscle contraction (2).
Who should take Multivitamins?
People whose diet may be restricted or unbalanced.
People with low calorie intake because of poor appetite Individuals with high energy requirements, for example, periods of heavy training Individuals on a very low calorie diet.
The elderly, those who omit whole food groups (2).
Women who may become pregnant should get 400 micrograms a day of Folic Acid. Women who are pregnant should take a prenatal Vitamin that includes iron or a separate iron supplement.
Adults age 50 or older should eat foods fortified with Vitamin B 12, such as fortified cereals or take a Multivitamin that contains B 12 or a separate B 12 supplement.
Adults age 65 and older should take 800 international units (IU) of Vitamin D daily to reduce the risk of falls (3).
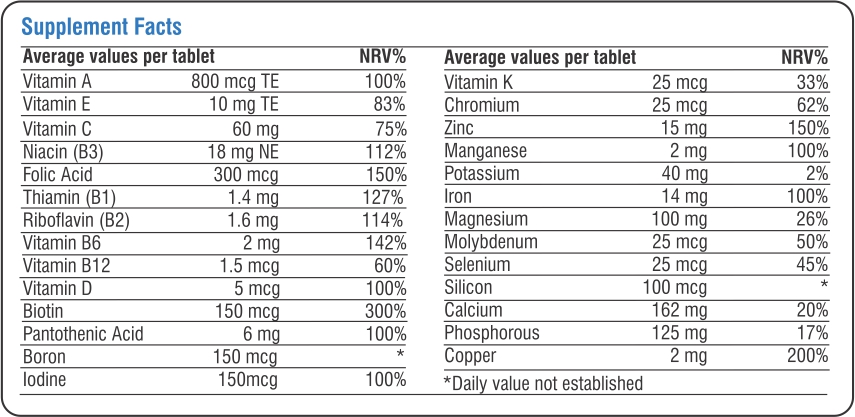
Life On Multi-Life has the perfect blend of essential Multivitamin and Multi mineral which provides improved health benefits. It has Anti-oxidants such as Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, Manganese, Chromium, Zinc. B-complex factors such as Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B5, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, Folic Acid. Vitamins like Biotin, Vitamin D3. Macro and Micro minerals like Copper, Magnesium and Molybdenum.
Life On Multi-Life is a perfect blend with essential Vitamins and minerals like Antioxidants, Micronutrients, Macro nutrients, B-complexes it prevents.
Vitamin A contributes to normal Iron metabolism, maintenance of normal mucous membranes, skin, normal vision, functioning of the immune system, process of cell specialisation (4).
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) plays a critical role in wound repair and healing/regeneration process as it stimulates collagen synthesis. Vitamin C protects against oxidation of isolated LDL by different types of oxidative stress and modification, lipid peroxidation of low density lipoproteins (LDL) are implicated in development of atherosclerosis (5).
Vitamin E, a potent peroxyl radical scavenger, is a chain-breaking antioxidant that prevents the propagation of free radical damage in biological membranes (6).
Riboflavin contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolism, functioning of the nervous system, maintenance of normal mucous membranes, red blood cells and skin (7).
Vitamin B12 contributes to normal functioning of the nervous system, homocysteine metabolism, function of the immune system, reduction of tiredness and fatigue and process of cell division (8).
Pantothenic acid contributes to normal synthesis and metabolism of steroid hormones, Vitamin D and some neurotransmitters, Vitamin D contributes to normal absorption and utilisation of Calcium and Phosphorus, maintenance of normal bones, muscle function, teeth (9).
Biotin contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolism, functioning of the nervous system, normal macronutrient metabolism maintenance of normal hair and mucus membrane (10).
Vitamin K contributes to normal blood clotting and maintenance of normal bone (11).
Zinc helps in maintaining healthy hair, nails and skin and promotes in maintaining the testosterone levels in the body (12).
Copper helps in maintaining the strong connective tissues all over the body, promotes in protecting the cells from oxidative stress (13).
Iron improves in formation of red blood cells, haemoglobin, energy metabolism and normal cognitive function; it contributes to oxygen transport in the body to reduce tiredness and fatigue. It increases the role in the process of cell division (14).
References
1.Multivitamins,www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a682882.html
2.Multivitamins - Minerals,the irish sports council, institute of sports.ie
3.Supplements: Nutrition in a pill, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/supplements/art-20044894
4.Vitamin A, http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims
5.Vitamin C in human health and disease is still a mystery? An overview
6.Vitamin E: beyond antioxidant function,ajcn. nutrition. org/ content /62/6/ 15 01 S.abstract
7.Riboflavin, http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims
8.Vitamin B12, http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims
9.Vitamin D, http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims
10.Biotin, http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims
11.Vitamin K, http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims
12.Zinc, http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims
13.Copper, http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims
14.Iron, http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims
